| |
||||
|
||||
CLIMATE OF ANCIENT EGYPT |
||||
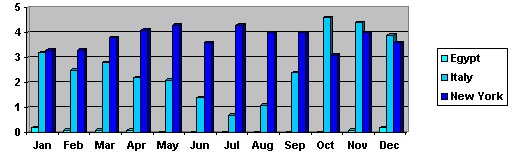
For thousands of years the climate of Egypt has been extremely consistent. It's been bone dry. More than other generally dry Mediterranean countries, Egypt is exceptionally
dry due to the almost complete absence of a rainy season. This aridity
has helped to perserve much of ancient Egypt's archeological remains.
It also inspired the Egyptians to develop the art of mummification.
And it leads to interesting speculations on the erosion patterns and
age of the Great Sphinx. |
||||
 |
||||
Avergage Monthly Precipitation in Inches
|
||||
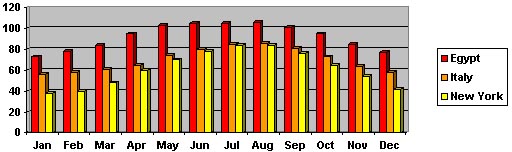
From April to November
the temperatures in Egypt are extremely hot with highs in July reaching
above 110° Fahrenheit in the shade. The other four months can be
fairly cool -- nightime temperatures may drop to near freezing. From
mid-February to mid-June a hot southeast wind often creates huge dust
storms that cover local plants. The rest of the year, a northwest wind
lessens the extreme heat of the day. |
||||
 |
||||
Average High Temperatures in Degrees Fahrenheit
|
||||
Home | Nile Valley | Dynasties | Wealth | Divinity | Temples | Hieroglyphs | Mysteries
|
||||